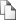ПРЕДИСЛОВИЕ / FOREWORD
Предлагаемый вниманию читателя сборник научных трудов представляет результаты, полученные в работе ученых многих научных организаций. Среди них читатель найдет новые данные, полученные в лабораториях биологического факультета и других факультетов Московского государственного университета имени М.В. Ломоносова, а также в других научных институтах. Публикацииохватывают широкий круг научных проблем, которые входят в проблематику наук о жизни, воде и Земле. В текущем году наша научная общественность отмечала 150-летний юбилей выдающегося русского ученого В.И. Вернадского. Его научное наследие включает в себя его весомый вклад в создание учения о биосфере. Труды авторов, образующие этот сборник, показывают, что современные ученые биофака МГУ и других научных учреждений продолжают исследовать проблемы биосферы. Эти работы продолжают традиции, заложенные В.И. Вернадским и другими выдающимися учеными.
В материалах данного сборника можно найти не только новые факты, но и новые обобщения. Это важно, поскольку развитие научных знаний дает основу для совершенствования университетского образования.
Данный сборник представит интерес для научных работников, преподавателей, студентов, аспирантов многих областей биологии, экологии, наук об окружающей среде. Приложение новых знаний на практике будет способствовать новому развитию и прогрессу в науке, образовании, служить для развития экономики и улучшения жизни людей.
Член-корреспондент РАН Е.А. Криксунов
Член-корреспондент РАН И.Ю. Чернов
Доктор биологических наук, профессор С.Н. Орлов
This collection of scientific works represents a broad spectrum of results of research activities of scientists of many scientific institutions. Among them, the reader will find new data obtained in laboratories of Faculty of Biology and various other faculties and departments of M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, of a number of scientific institutes. The publications cover a wide range of topics that include life sciences, water science, and geoscience. This year our science celebrated the 150th anniversary of the great Russian scientist, V.I. Vernadsky. His scientific heritage was his significant contribution to the science on the biosphere. The works of the authors represented in this volume demonstrate that the contemporary scientist keep on working on the issues of the biosphere. These works continue the scientific traditions of V.I. Vernadsky and other great scientists.
The volume includes not only new facts but also new ideas and concepts. This development of scientific knowledge will be useful in university education.
The volume will be of interest to scientists, professors and students who are focused on studies of many areas of biology, ecology, environmental science, including many disciplines. The application of the new knowledge will be a substantial contribution to development and progress of science, education, and welfare of people.
Corresponding Member of RAN E.A. Kriksunov
Corresponding Member of RAN I. Yu. Chernov
Professor S.N.Orlov
IMPACT OF ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS ON THE FORMATION OF TYPES OF DIGESTION IN ONTOGENESIS OF THE CASPIAN SAIGA
R.M. Khatsaeva
Federal State Institution of Science Institute A.N. Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution, Moscow, Russia, [email protected]
The saiga antelope (Saiga tatarica L., 1766) is a unique ancient ruminant animals living in the arid zone and exhibiting a high resistance to adverse climatic conditions. As a ruminant saiga has a complex four-chambered stomach and gastro-intestinal type of digestive system, which ensures a prosperous development in the harsh conditions of existence. In this regard, the study of reflection on the emergence of ecology in the ontogeny of the type of digestion in the saiga is relevant.
The material for these studies were the stomachs of fetuses, newborns, four-month and adult saiga harvested in the Caspian region. Complex was used histological, histochemical and biochemical methods.
The growth of the stomach is uneven. The greatest increase in its mass in the observed the early the fetal period to 60 days. Then there is a decrease in growth rate up to 105 days, coinciding with the difficulties in the forage (February-March), after which the growth rate increases again for the birth and continues to grow [1, 2].
In the early fetal period, the stomach has all four chambers. The highest chamber is the scar, then the growth rate of rennet is increased to 115 days is the equalization of their mass, the birth of the abomasum is the largest chamber. After that, there is a change of intensity of growth abomasum and rumen, and four months of age lambs have the second equalizing their weight. In adult animals, the highest chamber is the rumen, amounting to 65.1% by weight of the stomach, then the abomasum, the reticulum and the omasum [3].
By the early fetal period in all differentiated cells of the stomach mucosa, muscular and serous membranes, whose growth has been uneven. The early the fetal period the thickness of the mucosa than muscle. At the end of the early the fetal period - beginning the late the fetal period observed slowdown in the muscle membrane [1, 2, 3].
Since the mid the late fetal period the growth rate decreases mucosal and muscle - is increasing, which leads to the equalization of their thickness. Then there is a slowdown in the muscle membrane proventriculus transitional stage from the early - to the late the fetal period.
The mucous membrane of early fetuses involved in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism, as evidenced by the discovery there of a large amount of glycogen (fig. 1), lipase, alkaline and acid phosphatase, sulfated polysaccharides, proteins, and pepsin.
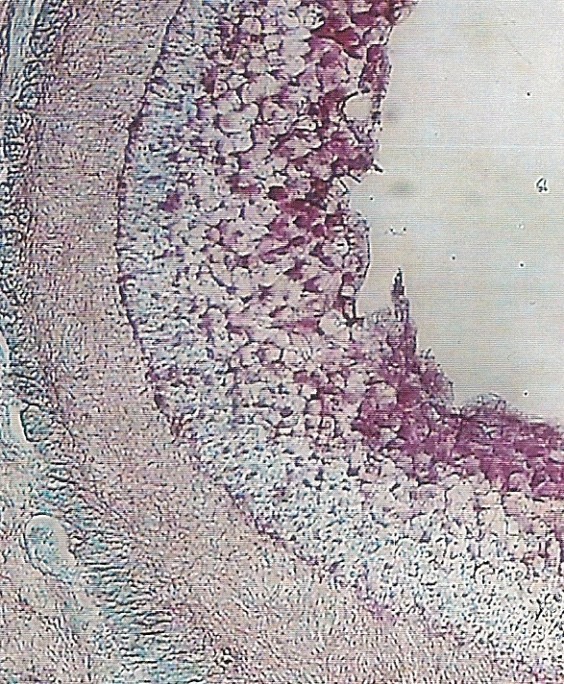
Fig. 1. Glycogen in the epithelial layer proventriculus early fruit saiga. SW. 100.
In the late the fetal period enzyme activity increases and the surface epithelial layer accumulate neutral glycoproteins and protein, forming a protective layer - glycocalyx. The enzyme activity and the nature of their location says the participation of proventriculus mucosa in the transport of substances, leading to an accumulation of contents in the cavity proventriculus [1, 2, 3].
This is evidenced by the formation of cavities in the epithelium of the proventriculus, contributing to the accumulation and excretion of substances into the body cavity. Apparently, the contents accumulated in the cavities of the proventriculus to the ingestion of the amniotic fluid are a reserve of trophy and biologically active substances to the fetus, thus expressing their participation in gomotrofic nutrition (fig. 2).
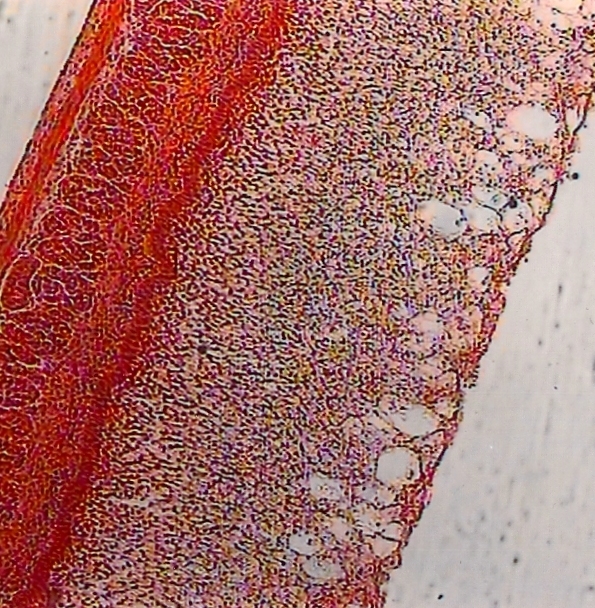
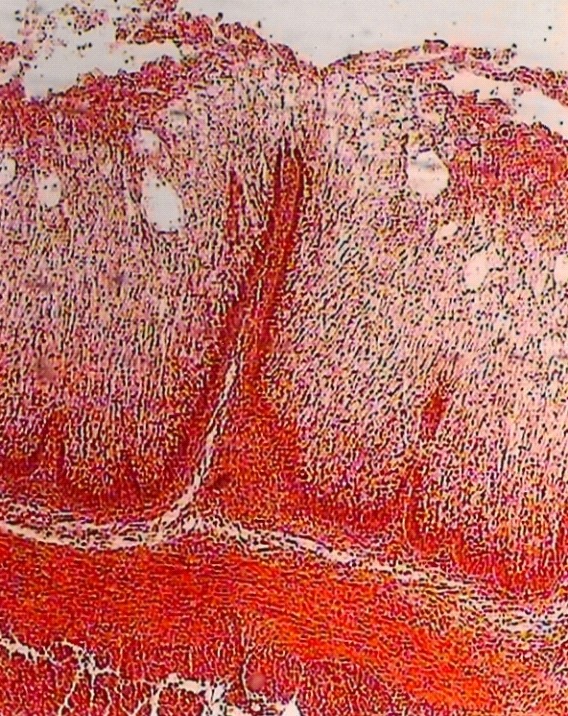
Fig. 2. Cavity in the epithelial layer proventriculus early fruit saiga. SW. 100.
Thus, the results of the study show that the development of the stomach and his camera at the saiga has the same laws that all ruminants. Along with this, the saiga has features, which consist in the fact that the development of gastric and cameras they already have in the uterine Time reflects ecological adaptation to assimilate voluminous coarse grass feed, creating greater severity of their gastrointestinal type of digestion, which makes them wild and domestic ruminants is distinguished from [3]. Consequently, revealed a pronounced Saiga type of digestion of ruminants adapted to assimilate voluminous coarse vegetable food, demonstrates the need to preserve their habitat and ecology of prey.
Literature
1. Khatsaeva R.M. Morphological and functional features of cells of the stomach of ruminants / / Zool. 2004. T. 83. Number 12. Pp. 1508-1516.
2. Khatsaeva R.M. Morphological features of the stomach into the ontogeny in relation to food specialization representatives Caprinae. Diss. Doctor. biol. Science. Moscow: OOO "11-th format." 2005. 433P.
3. Khatsaeva R.M. Morphological features of the stomach and its chambers in wild and domestic Caprinae due to food specialization / / Coll. Monograph. Book 2. Actual problems of chemistry, biology and medicine. Krasnoyarsk Research and Innovation Center. 2011. Pp. 231-263.
Summary
The present study shows that the development of the stomach and its cameras in saiga, already uterine time and throughout ontogeny, reflect ecological adaptation to assimilate voluminous forage grass, create a greater severity of their gastro-intestinal type of digestion, which makes them similar to and different from wild domestic ruminants. This demonstrates the need to maintain their ecological habitat and prey.
EXPERIMENTAL INTERDISCIPLINARY RESEARCH IN LIFE SCIENCE: MOLECULAR AND ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY, BIOPHYSICS. FROM FUNDAMENTAL BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH TO APPLICATIONS. SOME RESULTS AND BIBLIOGRAPHY
Orlov S.N., Kotelevtsev S.V., Novikov K.N., Selishcheva A.A., Akimova O.A., Ostroumov S.A.
M.V.Lomonosov Moscow State University, Vorobyevy Gory, Moscow; Universite de Montreal;
The goal of this publication is to present some of results of experimental research of interdisciplinary topics of life science in the Laboratory of Physico-Chemistry of biological membranes. The material is organized into 6 sections.
1. Results of S.N. Orlov and co-authors, examples:
Cell volume and monovalent ion transporters: their role in triggering and progression of the cell death machinery (Orlov S.N., et al., 2013).
Apoptosis involves many aspects of biochemical and biophysical phenomena in cell biology, including monovalent ion transfer across biological membranes. The studies of interconnections among those phenomena is of a significant interest.
Cell death is accompanied by the dissipation of electrochemical gradients of monovalent ions across the plasma membrane that, in turn, affects cell volume via modulation of intracellular osmolyte content. In various cell types, apoptotic and necrotic stimuli caused cell shrinkage and swelling, respectively. Thermodynamics predicts a cell type-specific rather than a ubiquitous impact of monovalent ion transporters on volume perturbations in dying cells, suggesting their diverse roles in the cell death machinery. Indeed, some recent data showed that apoptotic collapse may occur in the absence of cell volume changes and even follow cell swelling rather than shrinkage.
Moreover, side-by-side with cell volume adjustment, monovalent ion transporters contribute to cell death machinery engagement independently of volume regulation via cell type-specific signalling pathways. Thus, inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase by cardiotonic steroids (CTS) rescues rat vascular smooth muscle cells from apoptosis via a novel Na+i,K+i-mediated, Ca2+i-independent mechanism of excitation-transcription coupling. By contrast, CTS kill renal epithelial cells independently of Na+,K+-ATPase inhibition and increased [Na+]i/[K+]i ratio.
The molecular origin of [Na+]i/[K+]i sensors involved in the inhibition of apoptosis as well as upstream intermediates of Na+i/K+i-independent death signalling triggered by cardiotonic steroids (CTS) remain a subject for further research.
(based on: Orlov SN, Platonova AA, Hamet P, Grygorczyk R. Cell volume and monovalent ion transporters: their role in triggering and progression of the cell death machinery. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Apr 24. [Epub ahead of print]).
Bibliography of publications of Orlov S.N., selected:
1. Orlov SN, Platonova AA, Hamet P, Grygorczyk R. Cell volume and monovalent ion transporters: their role in triggering and progression of the cell death machinery. // Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Apr 24. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23615964
2. Parshina EY, Yusipovich AI, Platonova AA, Grygorczyk R, Maksimov GV, Orlov SN. Thermal inactivation of volume-sensitive K(+),Cl (-) cotransport and plasma membrane relief changes in human erythrocytes. // Pflugers Arch. 2013 Feb 2. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23377567 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
3. Orlov SN, Koltsova SV, Tremblay J, Baskakov MB, Hamet P. NKCC1 and hypertension: role in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle contractions and myogenic tone. // Ann Med. 2012 Jun;44 Suppl 1:S111-8. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2011.653395. Review. PMID: 22713139 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
4. Koltsova SV, Trushina Y, Haloui M, Akimova OA, Tremblay J, Hamet P, Orlov SN. Ubiquitous [Na+]i/[K+]i-sensitive transcriptome in mammalian cells: evidence for Ca(2+)i-independent excitation-transcription coupling. // PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038032. Epub 2012 May 29. PMID: 22666440 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
5. Koltsova SV, Akimova OA, Kotelevtsev SV, Grygorczyk R, Orlov SN. Hyperosmotic and isosmotic shrinkage differentially affect protein phosphorylation and ion transport. // Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;90(2):209-217. doi: 10.1139/y11-119. Epub 2012 Feb 2. PMID: 22300272 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
6. Platonova A, Koltsova SV, Hamet P, Grygorczyk R, Orlov SN. Swelling rather than shrinkage precedes apoptosis in serum-deprived vascular smooth muscle cells. // Apoptosis. 2012;17(5):429-438. doi: 10.1007/s10495-011-0694-x. PMID: 22249286 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
7. Akimova OA, Van Huysse J, Tremblay J, Orlov SN. Low efficiency of functional translation of ouabain-resistant 2-Na(+),K(+)-ATPase mRNA in C7-MDCK epithelial cells. // Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;90(1):83-8. doi: 10.1139/y11-113. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PMID: 22188474 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
8. Orlov SN. NKCC1 as an epigenetically regulated transporter involved in blood pressure elevation with age. // Am J Hypertens. 2011 Dec;24(12):1264. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2011.150. PMID: 22083447 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
9. Yusipovich AI, Zagubizhenko MV, Levin GG, Platonova A, Parshina EY, Grygorzcyk R, Maksimov GV, Rubin AB, Orlov SN. Laser interference microscopy of amphibian erythrocytes: impact of cell volume and refractive index. // J Microsc. 2011 Dec;244(3):223-229. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2011.03516.x. Epub 2011 Oct 17. PMID: 21999139 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
10. Orlov SN, Hamet P. [The search for a sensor of intracellular sodium involved in pathogenesis of hypertensive disease]. // Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2011;(7):45-50. Review. Russian. PMID: 21899092 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
11. Orlov SN, Churilov LP, Stroev IuI. [What is pathophysiology nowadays? The reflections of the participants of ISP-2010 Congress in Montreal]. // Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 2011 Apr-Jun;(2):3-12. Russian. PMID: 21847827 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
12. Platonova A, Koltsova S, Maksimov GV, Grygorczyk R, Orlov SN. The death of ouabain-treated renal epithelial C11-MDCK cells is not mediated by swelling-induced plasma membrane rupture. // J Membr Biol. 2011 Jun;241(3):145-54. doi: 10.1007/s00232-011-9371-9. Epub 2011 May 17. PMID: 21584679 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
13. Koltsova SV, Platonova A, Maksimov GV, Mongin AA, Grygorczyk R, Orlov SN. Activation of P2Y receptors causes strong and persistent shrinkage of C11-MDCK renal epithelial cells.// Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;301(2):C403-412. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00018.2011. Epub 2011 May 11. PMID: 21562307 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
14. Kol'tsova SV, Baskakov MB, Orlov SN. [Myogenic tone of blood vessels in health and disease: role of purinergic signaling system and Na+, K+ 2Cl+ cotransport]. // Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 2010 Oct-Dec;(4):3-10. Review. Russian. PMID: 21395111 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
15. Koltsova SV, Trushina YA, Akimova OA, Hamet P, Orlov SN. Molecular origin of Na(+)/Li(+) exchanger: Evidence against the involvement of major cloned erythrocyte transporters. // Pathophysiology. 2011 Jun;18(3):207-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2010.12.001. Epub 2011 Jan 17. PMID: 21247741 [PubMed]
16. Akimova OA, Lopina OD, Rubtsov AM, Hamet P, Orlov SN. Investigation of mechanism of p38 MAPK activation in renal epithelial cell from distal tubules triggered by cardiotonic steroids.// Biochemistry (Mosc). 2010;75(8):971-978. PMID: 21073417 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
17. Malekin SI, Kotelevtsev SV, Gavrilova SA, Fadyukova OE, Golubeva AV, Grinchenko MI, Koshelev VB, Kotelevtsev YV, Hamet P, Orlov SN. Long-term normalization of blood pressure in SHR and 1-kidney 1-clip rats by synthetic precursor of stable PAF analogue without systemic effects in normotensive rats.//Pathophysiology. 2011 Apr;18(2):151-157. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2010.08.001.PMID: 20888741 [PubMed]
18. Rebrov VG, Usanov DA, Usanov AD, Kotelevtsev SV, Orlov SN. Low-frequency magnetic radiation leads to the broadening of valent bonds in protein infrared spectra. // Pathophysiology. 2011 Apr;18(2):121-3. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 May 26. PMID: 20537876 [PubMed]
19. Orlov SN, Tremblay J, Hamet P. NKCC1 and hypertension: a novel therapeutic target involved in the regulation of vascular tone and renal function. // Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010 Mar;19(2):163-168. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283360a46. Review. PMID: 20061948 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
20. Orlov SN, Gossard F, Pausova Z, Akimova OA, Tremblay J, Grim CE, Kotchen JM, Kotchen TA, Gaudet D, Cowley AW, Hamet P. Decreased NKCC1 activity in erythrocytes from African Americans with hypertension and dyslipidemia. // Am J Hypertens. 2010 Mar;23(3):321-326.
21. Maximov G.V., Orlov S.N. [book] 1994 Transport of calcium ions under axon functioning: mechanisms and regulation. Moscow State Univ. Publ., Moscow, 87 p.
2. Results of S.V.Kotelevtsev and co-authors, examples.
Mutagenicity and genotoxicity of the sewage and industrial effluents (Glazer V.M., Kotelevtsev S.V., et al., 1990)
The Ames test was applied for the analysis of industrial effluents from cellulose production and sewage waters varying in the degree of purification. The method used a metabolic activation system from rat and fish liver with Salmonella strains TA 98 and TA 100. As a result, a strong direct mutagenic effect on strain TA 100 was discovered in samples which were taken after cellulose chlorination.
The multistage procedure of sewage water purification allows to remove practically completely the mutagenic substances. A simultaneous study of cytotoxic effects of industrial effluents on mammalian cells discovered that the mutagenic activity was exhibited in not toxic concentrations. The results demonstrated the urgency of a regular biological control of the genotoxicity of industrial effluents from the sulfate production of cellulose.
This summary is based on the publication: Glazer VM, Kotelevtsev SV, Stepanova LI, Abilev SK, Buevich GV, Bem AM. An evaluation in the Ames test of the mutagenicity of the sewage and industrial effluents from the Baikal Paper and Pulp Combine. // Nauchnye Doki Vyss Shkoly Biol Nauki. 1990;(1):101-109.
Bibliography of publications of S.V.Kotelevtsev, selected.
1. Orlov S.N., Thorin-Trescases N., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Kotelevtsev S.V. INVERSION OF THE INTRACELLULAR NA+/K+ RATIO BLOCKS APOPTOSIS IN VASCULAR SMOOTH MUSCLE AT A SITE UPSTREAM OF CASPASE-3. // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999. Т. 274. № 23. С. 16545-16552.
2. Lindstrm-Sepp P., Huuskonen S., Rnen T., Hnninen O., Kotelevtsev S., Stepanova L., Mikkelson P. TOXICITY AND MUTAGENICITY OF WASTE WATERS FROM BAIKALSK PULP AND PAPER MILL: EVALUATION OF POLLUTANT CONTAMINATION IN LAKE BAIKAL. // Marine Environmental Research. 1998. Т. 46. № 1-5. С. 273-277.
3. Whitehead A., Anderson S.L., Kuivila K.M., Orlando J.L., Kotelevtsev S. GENOTOXICITY IN NATIVE FISH ASSOCIATED WITH AGRICULTURAL RUNOFF EVENTS. //Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 2004. Т. 23. № 12. С. 2868-2877.
4.Orlov S.N., Aksentsev S.L., Kotelevtsev S.V. EXTRACELLULAR CALCIUM IS REQUIRED FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF PLASMA MEMBRANE INTEGRITY IN NUCLEATED CELLS. //Cell Calcium. 2005. Т. 38. № 1. С. 53-57.
5. Akimova O.A., Poirier M., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Kotelevtsev S.V. THE DEATH OF OUABAIN-TREATED RENAL EPITHELIAL CELLS: EVIDENCE AGAINST ANOIKIS OCCURRENCE. // Apoptosis. 2008. Т. 13. № 5. С. 670-680.
6. Orlov S.N., Grygorczyk R., Kotelevtsev S.V. DO WE KNOW THE ABSOLUTE VALUES OF INTRACELLULAR FREE CALCIUM CONCENTRATION? // Cell Calcium. 2003. Т. 34. № 6. С. 511-515.
7. Павлов Д.С., Смуров А.В., Ильяш Л.В., Маторин Д.Н., Клюев Н.А., Котелевцев С.В., Румак В.С., Смурова Т.Г. СОВРЕМЕННОЕ СОСТОЯНИЕ КОРАЛЛОВЫХ РИФОВ ЗАЛИВА НЯЧАНГ (ЮЖНЫЙ ВЬЕТНАМ) И ВОЗМОЖНЫЕ ПРИЧИНЫ НЕБЛАГОПОЛУЧИЯ СРЕДЫ ОБИТАНИЯ СКЛЕРАКТИНИЙ. // Биология моря. 2004. Т. 30. № 1. С. 60-67.
8. Остроумов С.А., Шестакова Т.В., Котелевцев С.В., Соломонова Е.А., Головня Е.Г., Поклонов В.А. ПРИСУТСТВИЕ МАКРОФИТОВ В ВОДНОЙ СИСТЕМЕ УСКОРЯЕТ СНИЖЕНИЕ КОНЦЕНТРАЦИЙ МЕДИ, СВИНЦА И ДРУГИХ ТЯЖЕЛЫХ МЕТАЛЛОВ В ВОДЕ. // Водное хозяйство России: проблемы, технологии, управление. 2009. № 2. С. 58-66.
9. Koltsova S.V., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Kotelevtsev S.V. EXCITATION-CONTRACTION COUPLING IN RESISTANCE MESENTERIC ARTERIES: EVIDENCE FOR NKCC1-MEDIATED PATHWAY // Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2009. Т. 379. № 4. С. 1080-1083.
10. Остроумов С.А., Котелевцев С.В., Шестакова Т.В., Колотилова Н.Н., Поклонов В.А., Соломонова Е.А. НОВОЕ О ФИТОРЕМЕДИАЦИОННОМ ПОТЕНЦИАЛЕ: УСКОРЕНИЕ СНИЖЕНИЯ КОНЦЕНТРАЦИЙ ТЯЖЕЛЫХ МЕТАЛЛОВ (PB, CD, ZN, CU) В ВОДЕ В ПРИСУТСТВИИ ЭЛОДЕИ. // Экологическая химия. 2009. № 18. С. 111.
11. Koltsova S.V., Lavoie J.L., Tremblay J., Grygorczyk R., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Maximov G.V., Kotelevtsev S.V. MYOGENIC TONE IN MOUSE MESENTERIC ARTERIES: EVIDENCE FOR P2Y RECEPTOR-MEDIATED, NA+, K+, 2CL- COTRANSPORT-DEPENDENT SIGNALING. // Purinergic Signalling. 2009. Т. 5. № 3. С. 343-349.
12. Kotelevtsev S.V., Hanninen O.O.P., Lindstrm-Seppa P.A., Huskon S.E., Stepanova L.I., Glaser V.M., Beim A.M. Mutagenicity of bleached and unbleached effluents from Baikalsk pulp and paper mill at Lake Baikal, Russia. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management. 2000. Т. 3. С. 95-104.
13. Stepanova L.I., Lindstrm-Sepp P., Hnninen O.O.P., Kotelevtsev S.V., Glaser V.M., Novikov C.N. LAKE BAIKAL: BIOMONITORING OF PULP AND PAPER MILL WASTE WATER. // Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management. 2000. Т. 3. С. 259.
14. Stepanova L.I., Glaser V.M., Savinova T.I., Kotelevtsev S.V., Savva D. ACCUMULATION OF MUTAGENIC XENOBIOTICS IN FRESH WATER (LAKE BAIKAL) AND MARINE (HORNOYA ISLAND) ECOSYSTEMS. // Ecotoxicology. 1999. Т. 8. № 2. С. 83-96.
15. Pavlov D.S., Kluyev N.A., Rumak V.S., Smurov A.V., Smurova T.G., Il'yash L.V., Matorin D.N., Kotelevtsev S.V. PRESENT-DAY STATE OF CORAL REEFS OF NHA TRANG BAY (SOUTHERN VIETNAM) AND POSSIBLE REASONS FOR THE DISTURBANCE OF HABITATS OF SCLERACTINIAN CORALS. // Russian Journal of Marine Biology. 2004. Т. 30. № 1. С. 43-50.
16. Саратовских Е.А., Глазер В.М., Костромина Н.Ю., Котелевцев С.В. ГЕНОТОКСИЧНОСТЬ ПЕСТИЦИДОВ В ТЕСТЕ ЭЙМСА И ИХ СПОСОБНОСТЬ К ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ КОМПЛЕКСОВ С ДНК. // Экологическая генетика. 2007. Т. V. № 3. С. 46-54.
17. Котелевцев С.В., Пономарева Л.В. ИНДУКЦИЯ С ПОМОЩЬЮ ПОЛИЦИКЛИЧЕСКИХ УГЛЕВОДОРОДОВ АКТИВНОСТИ МОНООКСИГЕНАЗ В ТКАНЯХ РЫБ И ЕЕ ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЕ ДЛЯ БИОМОНИТОРИНГА ЗАГРЯЗНЕННЫХ ВОД. //Экспериментальная онкология. 1987. № 5. С. 46. 18.
18. Котелевцев С.В., Степанова Л.И. БИОТЕСТИРОВАНИЕ КАНЦЕРОГЕННЫХ И МУТАГЕННЫХ СОЕДИНЕНИЙ В ВОДНЫХ СИСТЕМАХ. //Российский химический журнал. 1994. Т. 38. С. 42.
19. Котелевцев С.В., Пономарева Л.В., Новиков К.Н. ИММУНОХИМИЧЕСКИЙ АНАЛИЗ ИНДУКЦИИ ИЗОФОРМ ЦИТОХРОМА Р-450 В ПЕЧЕНИ ПРЕСНОВОДНЫХ РЫБ 3-МЕТИЛХОЛАНТРЕНОМ, B-НАФТАФЛАВОНОМ И АРОХЛОРОМ 1254. // Биологические науки. 1990. № 5. С. 23.
20. Kotelevtzev S.V., Nagdaliev F.F., Sadchikov A.P. Bio-assay and bioindication at ecological analysis of the environment. Publishers: Alteks, Moscow, 2011, 174 p.
21. Kotelevtsev S.V., Matorin D.N., Sadchikov A.P. Ecological-Toxicological analysis of plant communities in aquatic ecosystems. Altex Press, Moscow. 2012. 182 p.
3. Results of K.N.Novikov and co-authors, examples.
Changes in chemiluminescence of whole blood of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients treated with Hypoxen; effects of fullerenes (C ) on blood chemiluminescence (Novikov et al., 2012).
Summary of a research project. BACKGROUND: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an inflammatory disease associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of Hypoxen treatment and the effect of fullerenes (HyFnC ) on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in patients' blood. MATERIAL/METHODS: Reactive oxygen species ROS production in blood was estimated using chemiluminescence (CL) measurement with chemiluminescence amplifiers, namely: luminol (LM), LM + zymosan (ZM) or lucigenin (LC) in the presence or absence of hydrated fullerenes (HyFnC) added to blood in low concentrations. RESULTS: In all the patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in remission phase with Hypoxen prescription, the LM-dependent CL (LM-CL) with ZM and LC-enhanced CL (LC-CL) decreased after the treatment. Parameters of chemiluminescence and effects of fullerenes (HyFnC ) upon them depended on blood state. Addition of fullerenes HyFnC to blood decreased data scattering and helped to improve discrimination between different groups of patients. Using the discriminator analysis, we found the most important time-points in the kinetic curves of chemiluminescence for>
This summary is based on:
Novikov KN, Berdnikova NG, Novikov AK, Lyusina OY, Muhitova OG, Yablonskaya OI, Minh HD, Voeikov VL. Changes in chemiluminescence of whole blood of COPD patients treated with Hypoxen and effects of C fullerenes on blood chemiluminescence. // Med Sci Monit. 2012; 18(2): BR76-83.
Bibliography of Novikov K.N. et al. (publications, selected):
1. Ракитин Г.В., Генералова В.К., Кисарева Е.В., Чалкин С.Ф., Воейков В.Л., Новиков К.Н. СПОСОБ ОЧИСТКИ ВОДНЫХ РАСТВОРОВ // патент на изобретение RUS 2120410
2. Баранчиков В.И., Воейков В.Л., Волков А.В., Кийко Ю.И., Кондаков С.Э., Новиков К.Н., Розенталь В.М. СПОСОБ ДИАГНОСТИКИ ИНДИВИДУАЛЬНОЙ ЧУВСТВИТЕЛЬНОСТИ ОРГАНИЗМА К ПИЩЕВЫМ ПРОДУКТАМ //патент на изобретение RUS 2152616 19.05.1999
3. Воейков В.Л., Кондаков С.Э., Новиков К.Н., Химич М.В. СПОСОБ ОБРАБОТКИ ПИТЬЕВОЙ МИНЕРАЛЬНОЙ ВОДЫ И НАПИТКА НА ЕЕ ОСНОВЕ. // патент на изобретение RUS 2218055 26.07.2001
4. Воейков В.Л., Вокуев И.А., Новиков К.Н., Сюч Н.И. СПОСОБ КОНТРОЛЯ ЗА СОСТОЯНИЕМ БОЛЬНЫХ ИШЕМИЧЕСКОЙ БОЛЕЗНЬЮ СЕРДЦА В ХОДЕ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ВНУТРИВЕННОЙ НИЗКОИНТЕНСИВНОЙ ЛАЗЕРНОЙ ТЕРАПИЕЙ // патент на изобретение RUS 2127881
5. Воейков В.Л., Волков А.В., Кондаков С.Э., Калинин А.И., Новиков К.Н., Розенталь В.М., Асфарамов Р.Р.О., Воейкова Т.А. СПОСОБ ОЧИСТКИ ВОДЫ ОТ РАДИКАЛЬНЫХ И ИОН-РАДИКАЛЬНЫХ ЧАСТИЦ // патент на изобретение RUS 2167107 17.10.2000
6. Воейков В.Л., Волков А.В., Кондаков С.Э., Новиков К.Н., Розенталь В.М.СРЕДСТВО ДЛЯ ОЧИСТКИ ВОДЫ ОТ РАДИКАЛЬНЫХ И ИОН-РАДИКАЛЬНЫХ ЧАСТИЦ //патент на изобретение RUS 2166991 17.10.2000
7 Orlov S.N., Aksentsev S.L., Novikov K.N., Konev S.V. THE REGULATION OF CELL VOLUME: THE MECHANISMS OF INTRACELLULAR SIGNALLING // Российский физиологический журнал им. И.М. Сеченова. 1997. Т. 83. № 7. С. 1-18.
8. Воейков В.Л., Волков А.В., Кондаков С.Э., Новиков К.Н., Розенталь В.М., Асфарамов Р.Р.О., Воейкова Т.А. УСТРОЙСТВО ДЛЯ ОЧИСТКИ ПИТЬЕВОЙ ВОДЫ ОТ РАДИКАЛЬНЫХ И ИОН-РАДИКАЛЬНЫХ ЧАСТИЦ И ЕЕ КОНДИЦИОНИРОВАНИЯ // патент на изобретение RUS 2179531 13.04.2000.
9. Sirota T.V., Miroshnikov A.I., Novikov K.N. ANALYSIS OF PRO/ANTIOXIDANT PROPERTIES OF WATER AND WATER SOLUTIONS // Biophysics. 2010. Т. 55. № 6. С. 911-915.
13. Cиpота Т.В., Миpошников А.И., Новиков К.Н. ОЦЕНКА ПPО/АНТИОКCИДАНТНЫX CВОЙCТВ ВОДЫ И ВОДНЫX PАCТВОPОВ // Биофизика. 2010. Т. 55. № 6. С. 990-995.
14 Воейков В.Л., Асфарамов P.P., Виленская Н.Д., Новиков К.Н. СОБСТВЕННОЕ ИЗЛУЧЕНИЕ ЦЕЛЬНОЙ КРОВИ ОТРАЖАЕТ ЕЕ ИММУННЫЕ И ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЕ СВОЙСТВА // Альманах клинической медицины. 2006. № 12. С. 12-12.
15. Novikov K.N., Lyusina O.Y., Muhitova O.G., Yablonskaya O.I., Minh H.D., Voeikov V.L., Berdnikova N.G., Novikov A.K. CHANGES IN CHEMILUMINESCENCE OF WHOLE BLOOD OF COPD PATIENTS TREATED WITH HYPOXEN® AND EFFECTS OF C60 FULLERENES ON BLOOD CHEMILUMINESCENCE // Medical Science Monitor. 2012. Т. 18. № 2. С. BR76-BR83.
16. Novikov K.N., S.V. Kotelevtsev, Yu.P.Kozlov. The free-radical processes in biological systems under the influence of environmental factors. - Moscow: Publishing House of People's Friendship University, 2011. - 199 p. ISBN 978-5-209-03659-3.
4. Results obtained by A.A. Selishcheva and co-authors, examples.
Effects of liposomes of different phospholipid composition on the induction of respiratory burst in human blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages (Selishcheva et al. 2001).
Summary: Liposomes made from phosphatidylcholine (PC) or PC-fatty acid ester mixtures have been shown to induce an activation of the respiratory burst in human blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages (AM). Incorporation of 1,2-diacylglycerol or arachidonic acid into phosphatidylcholine (PC) liposomes significantly enhanced the effect. In the case of alveolar macrophages (AM), the effect of phosphatidylcholine (PC) liposomes was similar to those of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and the ionophore A 23187, while in monocytes, PMA and the ionophore A 23187 induced a stronger respiratory burst than phosphatidylcholine (PC) liposomes. In the presence of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), higher liposomal concentrations were required to produce the maximum activation of the respiratory burst in both types of cells.
The summary is based on: Selishcheva AA, Atruz OM, Sorokoumova GM, Skrjabin GA, Vasilenko IA, Chuchalin AG. Effects of liposomes of different phospholipid composition on the induction of respiratory burst in human blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages. // Membr Cell Biol. 2001;14(5):637-647.
Bibliography of Selishcheva A.A. et al.: publications, selected :
1. Sosunov V., Mischenko V., Majorov K., Apt A., Eruslanov B., Svetoch E., Shakina Y., Sorokoumova G., Selishcheva A., Stern N. ANTIMYCOBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF BACTERIOCINS AND THEIR COMPLEXES WITH LIPOSOMES // Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2007. Т. 59. № 5. С. 919.
2. Istarova T.A., Sorokoumova G.M., Semenova M.G., Belyakova L.E., Polikarpov Y.N., Anokhina M.S., Selishcheva A.A. EFFECT OF PH ON THE INTERACTIONS OF SODIUM CASEINATE WITH SOY PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN RELATION TO THE FOAMING ABILITY OF THEIR MIXTURES // Food Hydrocolloids. 2005. Т. 19. № 3. С. 429-440.
3. Сорокоумова Г.М., Андреевская С.М., Смирнова Т.Г., Петрова Е.Е., Жогина Ю.А., Калашникова Т.Ю., Черноусова Л.Н., Селищева А.А., Швец В.И. ВЛИЯНИЕ ЛИПОСОМ РАЗЛИЧНОГО ЛИПИДНОГО СОСТАВА НА РОСТ MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS H37RV IN VITRO // Бюллетень экспериментальной биологии и медицины. 2009. Т. 148. № 11. С. 550-553.
4. Tiourina O.P., Selishcheva A.A., Larionova N.I., Sharf T.V., Sorokoumova G.M., Shvets V.I. COMPLEXING OF BASIC PANCREATIC PROTEINASE INHIBITOR WITH SOYBEAN PHOSPHOLIPID MULTILAMELLAR VESICLES // Biochemistry (Moscow). 2001. Т. 66. № 3. С. 340-344.
5. Минина А.В., Сорокоумова Г.М., Селищева А.А., Маликова Н.М., Калашникова Т.М., Швец В.И. Биофизика. 2004. Т. 49. № 4. С. 674.
6. Tiourina O., Sharf T., Balkina A., Selischeva A., Sorokoumova G., Larionova N., Ollivon M.
INTERACTION OF THE WATER-SOLUBLE PROTEIN APROTININ WITH LIPOSOMES: GEL-FILTRATION, TURBIDITY STUDIES, AND 31P NMR STUDIES // Journal of Liposome Research. 2003. Т. 13. № 3-4. С. 213-229.
7. Utkina E.A., Antoshina S.V., Sorokoumova G.M., Rogozhkina E.A., Shvets V.I., Selishcheva A.A. ISOFLAVONES DAIDZEIN AND GENISTEIN: PREPARATION BY ACID HYDROLYSIS OF THEIR GLYCOSIDES AND THE EFFECT ON PHOSPHOLIPID PEROXIDATION // Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry. 2004. Т. 30. № 4. С. 385-390.
8. Tiourina O.P., Selischeva A.A., Larionova N.I., Martynova O.M., Sorokoumova G.M., Shvets V.I. INTERACTION OF TRYPSIN WITH MULTILAMELLAR VESICLES OF SOYBEAN LIPIDS // Biochemistry (Moscow). 2000. Т. 65. № 9. С. 1049-1054.
9. Balkina A.S., Larionova N.I., Selischeva A.A., Sorokoumova G.M. INTERACTION OF NATIVE BOWMAN-BIRK SOYBEAN PROTEASE INHIBITOR AND ITS HYDROPHOBIZED DERIVATIVE WITH MULTILAMELLAR VESICLES OF SOYBEAN PHOSPHOLIPIDS // Biochemistry (Moscow). 2006. Т. 71. № 1. С. 84-89. 10. Sorokoumova G.M., Selishcheva A.A., Tiurina O.P., Alekseeva S.G., Martynova O.M., Sharf T.V., Shvets V.I. EFFECT OF WATER SOLUBLE NON-MEMBRANE PROTEINS ON THE PHOSPHOLIPID STRUCTURE // Биофизика. 2002. Т. 47. № 2. С. 268-276.
11. Мартынова О.М., Сорокоумова Г.М., Селищева А.А., Алексеева С.Г., Тюрина О.П., Швец В.И. // Бюллетень экспериментальной биологии и медицины. 2000. Т. 129. С. 159.
12. Минина А.В., Маликова Н.М., Сорокоумова Г.М., Селищева А.А., Швец В.И. ПОЛУЧЕНИЕ И ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ ЛИПОСОМ РАЗЛИЧНОГО СОСТАВА С ИЗОНИАЗИДОМ // Бюллетень экспериментальной биологии и медицины. 2004. Т. 137. № 1. С. 24.
13. Balkina A.S., Larionova N.I., Selischeva A.A., Sorokoumova G.M., Ollivon M. ENCAPSULATION OF BOWMAN-BIRK SOYBEAN PROTEINASE INHIBITOR WITHIN ZWITTERIONIC PHOSPHOLIPID MULTILAMELLAR VESICLES // Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2006. Т. 16. № 4. С. 301-306.
14. Балкина А.С., Селищева А.А., Ларионова Н.И. ЛИПОСОМАЛЬНЫЕ ФОРМЫ БЕЛКОВЫХ ИНГИБИТОРОВ ПРОТЕИНАЗ: ПОЛУЧЕНИЕ И СПЕЦИФИЧЕСКАЯ АКТИВНОСТЬ // Биомедицинская химия. 2008. Т. 54. № 5. С. 441.
15. Корженевский Д.А., Селищева А.А., Савельев С.В. ПОДХОД К ИДЕНТИФИКАЦИИ МОЛЕКУЛЯРНЫХ ФРАКЦИЙ ФОСФОЛИПИДОВ ЭРИТРОЦИТОВ ЧЕЛОВЕКА МЕТОДОМ ВЭЖХ С МАСС-СПЕКТРОМЕТРИЧЕСКИМ ДЕТЕКТИРОВАНИЕМ // Биомедицинская химия. 2010. Т. 56. № 6. С. 747-757.
16. Балкина А.С., Селищева А.А., Сорокоумова Г.М., Ларионова Н.И. ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЕ НАТИВНОГО И ГИДРОФОБИЗОВАННОГО ПРЕПАРАТОВ СОЕВОГО ИНГИБИТОРА ПРОТЕИНАЗ ТИПА БАУМАНА-БИРК С МУЛЬТИЛАМЕЛЛЯРНЫМИ ВЕЗИКУЛАМИ СОЕВЫХ ФОСФОЛИПИДОВ // Биохимия. 2006. Т. 71. № 1. С. 103-110.
17. Tiourina O.P., Sharf T.V., Selishcheva A.A., Sorokoumova G.M., Shvets V.I., Larionova N.I. COMPLEXING OF BASIC PANCREATIC PROTEINASE INHIBITOR WITH SOYBEAN PHOSPHOLIPID MULTILAMELLAR VESICLES // Биохимия. 2001. Т. 66. № 3. С. 419-424.
18. Трошкина О.А., Салина Е.Г., Сорокоумова Г.М., Капрельянц А.С., Селищева А.А. ВЛИЯНИЕ ЛИПОСОМ НА РОСТ И ЧУВСТВИТЕЛЬНОСТЬ MYCOBACTERIUM SMEGMATIS К ИЗОНИАЗИДУ // Прикладная биохимия и микробиология. 2007. Т. 43. № 1. С. 47-52.
19. Sorokoumova G.M., Vostrikov V.V., Rogozhkina E.A., Selishcheva A.A., Kalashnikova T.Yu., Shvets V.I., Golyshevskaya V.I., Martynova L.P., Erokhin V.V. BACTERIOSTATIC ACTIVITY AND DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS OF RIFAMPICIN IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION AND LIPOSOMAL COMPOSITION // Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 2008. Т. 42. № 8. С. 475-478.
20. Kornilova Z.Kh., Selishcheva A.A., Perel'man M.I. EFFECT OF PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE LIPOSOME ON REGENERATION OF SURGICAL WOUND IN GUINEA PIG LUNG // Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2001. Т. 131. № 2. С. 191-194.
5. Results obtained by O.A. Akimova and co-authors, examples.
Key words: C7-MDCK CELLS, SIGNALING, CARDIOTONIC STEROIDS, OUABAIN-TREATED CELLS, NA+,K +,CL- COTRANSPORT, ATP-TREATED, C11-MDCK CELLS, RENAL EPITHELIAL CELLS, Apoptosis, NA +,K+-ATPASE, C-FOS EXPRESSION, CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE PATHOGENESIS, OUABAIN, PURINERGIC INHIBITION, STRESS-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASES, 11 ISOZYME, Proteomics, Hypertension,
Bibliography of Akimova O.A. et al. (selected).
1. Akimova O.A., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Lopina O.D., Bagrov A.Y., Kamernitsky A.V.
CARDIOTONIC STEROIDS DIFFERENTIALLY AFFECT INTRACELLULAR NA+ AND [NA+]I/[K+]I-INDEPENDENT SIGNALING IN C7-MDCK CELLS. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005. Т. 280. № 1. С. 832-839.
2. Akimova O.A., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Lopina O.D. SEARCH FOR INTERMEDIATES OF NA+,K+-ATPASE-MEDIATED [NA+]I/[K+]I-INDEPENDENT DEATH SIGNALING TRIGGERED BY CARDIOTONIC STEROIDS. Pathophysiology. 2005. Т. 12. № 2. С. 125-135.
3. Akimova O.A., Pchejetski D., Hamet P., Orlov S.N. MODEST INTRACELLULAR ACIDIFICATION SUPPRESSES DEATH SIGNALING IN OUABAIN-TREATED CELLS. Pflgers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 2006. Т. 451. № 4. С. 569-578.
4. Akimova O.A., Mongin A.A., Hamet P., Orlov S.N. THE RAPID DECLINE OF MTT REDUCTION IS NOT A MARKER OF DEATH SIGNALING IN OUABAIN-TREATED CELLS. Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2006. Т. 52. № 8. С. 71-77.
5. Akimova O.A., Grygorczyk A., Bourcier N., Orlov S.N., Bundey R.A., Insel P.A., Gekle M. TRANSIENT ACTIVATION AND DELAYED INHIBITION OF NA+,K +,CL- COTRANSPORT IN ATP-TREATED C11-MDCK CELLS INVOLVE DISTINCT P2Y RECEPTOR SUBTYPES AND SIGNALING MECHANISMS. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006. Т. 281. № 42. С. 31317-31325.
6. Akimova O.A., Poirier M., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Kotelevtsev S.V. THE DEATH OF OUABAIN-TREATED RENAL EPITHELIAL CELLS: EVIDENCE AGAINST ANOIKIS OCCURRENCE. Apoptosis. 2008. Т. 13. № 5. С. 670-680.
7. Akimova O.A., Hamet P., Orlov S.N. [NA+]I/[K+]I-INDEPENDENT DEATH OF OUABAIN-TREATED RENAL EPITHELIAL CELLS IS NOT MEDIATED BY NA +,K+-ATPASE INTERNALIZATION AND DE NOVO GENE EXPRESSION. Pflgers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 2008. Т. 455. № 4. С. 711-719.
8. Orlov S.N., Haloui M., Taurin S., Akimova O.A., Guo D.F., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Dulin N.O. [NA+]I-INDUCED C-FOS EXPRESSION IS NOT MEDIATED BY ACTIVATION OF THE 5-PROMOTER CONTAINING KNOWN TRANSCRIPTIONAL ELEMENTS. FEBS Journal. 2007. Т. 274. № 14. С. 3557-3567.
9. Akimova O.A., Dolgova N.V., Mast N.V., Rubtsov A.M., Lopina O.D. REVEALING OF PROTEINS INTERACTING WITH NA,K-ATPASE. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2003. Т. 68. № 9. С. 1040-1047.
10. Akimova O., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Orlov S.N. THE NA+/K+-ATPASE AS [K+]O SENSOR: ROLE IN CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE PATHOGENESIS AND AUGMENTED PRODUCTION OF ENDOGENOUS CARDIOTONIC STEROIDS. Pathophysiology. 2006. Т. 13. № 4. С. 209-216.
11. Dolgova N.V., Kamanina Yu.V., Rubtsov A.M., Lopina O.D., Akimova O.A., Orlov S.N. A PROTEIN WHOSE BINDING TO NA,K-ATPASE IS REGULATED BY OUABAIN. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2007. Т. 72. № 8. С. 863-871.
12. Akimova O.A., Orlov S.N., Taurin S., Dulin N.O. PURINERGIC INHIBITION OF NA+,K+,CL- COTRANSPORT IN C11-MDCK CELLS: ROLE OF STRESS-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASES. Purinergic Signalling. 2008. Т. 4. № 2. С. 183-191.
13. Долгова Н.В., Каманина Ю.В., Акимова О.А., Орлов С.Н., Рубцов A.M., Лопина О.Д. БЕЛОК, СВЯЗЫВАНИЕ КОТОРОГО С NA,K-АТРАЗОЙ РЕГУЛИРУЕТСЯ УАБАИНОМ. Биохимия. 2007. Т. 72. № 8. С. 1061-1071.
14. Dolgova N., Mast N., Akimova O., Rubtsov A., Lopina O. PROTEINS BINDING TO 11 ISOZYME OF NA,K-ATPASE. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2003. Т. 986. С. 527-529.
15. Akimova O.A., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Orlov S.N., Lopina O.D. ALTERED PHOSPHORYLATION OF RRXS*/T* MOTIF IN OUABAIN-TREATED RENAL EPITHELIAL CELLS IS NOT MEDIATED BY INVERSION OF THE [NA] I/[K+]I RATIO. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2008. Т. 21. № 4. С. 315-324.
16. 2006. Akimova O.A., Hamet P., Orlov S.N. Proteomics-based identification of intermediates of [Na+]i/[K+]i-independent signaling triggered by cardiotonic steroids (CTS). Journal of Hypertension, [издательство Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Ltd. (United States)], 2006. том 24, с. S349-S349
17. 2012. Koltsova S.V., Trushina Y.A., Haloui M., Akimova O.A., Tremblay J., Hamet P., Orlov S.N.Ubiquitous [Na+]I/[K+]I-sensitive transcriptome mammalian cells: evidence for Ca2+I-independent excitation-transcription coupling. PloS One. [издательство Public Library of Science (United States)]. 2012. DOI.
6. Results obtained by S.A.Ostroumov and co-authors, examples.
Membrane-active, membranotropic xenobiotics and chemical-biotic interactions.
Membrane-active and membranotropic xenobiotics may enter the environment, in which case they become chemical pollutants. Examples of membranotropic pollutants are synthetic surfactants (surface active substances, surface-active agents exemplified by SDS, Triton X-100, and tetradecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, TDTMA). The role of these chemicals as ecotoxicants was not studied sufficiently to assess their environmental hazards. A series of new experiments to assess the potential environmental hazards from these membranotropic xenobiotics was run. In addition to that, some studies of other ecotoxicants were made as well. Moreover, experiments were run toward developing new biotechnologies for alleviating issues of ecotoxicant pollution of aquatic environment. The results contributed to ecotoxicological aspects of water science, and chemical-biotic interactions.
Bibliography. The summary is based on publications of Ostroumov S.A. et al., including, e.g.:
1. Ostroumov S.A., Kotelevtsev S.V. Toxicology of nanomaterials and environment // ECOLOGICA, 2011, v.18, № 61, p. 3-10.
2. Kotelevtsev S.V., Poklonov V.A., Sergeev V.A., Traore B., Glazer V.M., Ostroumov S.A. Mutagenic and carcinogenic chemicals in environmental samples of some agricultural areas in Africa // // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, vol.18, 2013, p. 53.
3.Остроумов C.А., Данилова В.Н., Ермаков В.В., Камнев А.Н., Колесов Г.М., Котелевцев С.В., Крупина М.В., Орлов С.Н., Сапожников Д.Ю., Сизов А.Д., Тропин И.В., Хушвахтова С.Д. Изучение накопления мембраноактивных и генотоксичных металлов в водных беспозвоночных: перспективы для мониторинга и новых технологий ремедиации // Биогеохимия в народном хозяйстве: фундаментальные основы ноосферных технологий. Материалы 6-й международной биогеохимической школы. 22-25 сентября 2008 г. Астрахань. Изд-во АГТУ (Астраханского гос. технического ун-та). Ред. В.Ф.Зайцев. 2008. С.129-130.
4. Ostroumov S.A., Danilova V.N., Ermakov V.V., Zubkova E.I., Kamnev A.N., Kolesov G.M., Kotelevtsev S.V., Krupina M.V., Lazareva E.V., Orlov S.N., Sapozhnikov D.Y., Solomonova E.A., Smurov A.V., Toderas I.K., Hushvakhtova S.D. Studying interaction of membranoactive and genotoxic substances with aquatic organisms / / 3rd Congress of Toxicologists of Russia, 2-5 December 2008, Moscow. Abstracts / Ed. by G.G. Onishchenko, and B.A. Kurlyandsky / Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russian Federation, Moscow, 2008, p.204 – 205.
5. Kotelevtsev S., Orlov S., Ostroumov S. Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions. 2009. Vol. 13. p.186-187.
6. Kotelevtsev S.V., Orlov S.N., Ostroumov S. Studying symbiotic associations (associative symbiosis) in microbial biocoenoses of aquatic bodies. (Review of the book: O.V. Bukharin, N.V. Nemtseva «Microbiology of biocoenoses of natural aquatic bodies»). - Ecology of surroundings and safety of vital activity, 2008. No.5, p. 84-86.
7. Остроумов С.А., Колесов Г.М., Котелевцев С.В., Моисеева Ю.А., Казаков Г.Ю. К изучению тяжелых металлов (включая хром и кобальт) в модельной водной экосистеме с использованием нейтронно-активационного анализа // Токсикологический вестник, 2010. № 6, с. 53-56.
8. Остроумов С.А., Тодераш И.К., Зубкова Е.И., Котелевцев С.В., Ермаков В.В., Крупина М.В., Ене А., Микус А.А., Билецки Л.И., Бряхнэ А., Мирон A. Биогенная миграция меди в водных экосистемах // Buletinul Academiei de stiinte a Moldovei. Life Sciences, 2009. № 3, с. 4-21.
9. Остроумов С.А., Колесов Г.М., Поклонов В.А., Котелевцев С.В. Водный макрофит как фактор потенциального концентрирования: взаимодействие с наночастицами металла // Экологическая химия, 2009, том 18, № 4, с. 222-228.
10. Остроумов С.А., Капица А.П., Котелевцев С.В., Головня Е.Г., Горшкова О.М., Лазарева Е.В., МакКатчеон С., Соломонова Е.А., Шестакова Т.В. Инновационная фитотехнология: вклад в наилучшие доступные технологии комплексного контроля и предотвращение загрязнения воды // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2009 том 13, с. 101-103.
11. Остроумов С.А., Котелевцев С.В., Шестакова Т.В., Колотилова Н.Н., Поклонов В.А., Соломонова Е.А. Новое о фиторемедиационном потенциале: ускорение снижения концентраций тяжелых металлов (Pb, Cd, Zn, Cu) в воде в присутствии элодеи // Экологическая химия, 2009, том 18, № 2, с. 111-119.
12. Остроумов С.А., Котелевцев С.В. О роли и месте концепций экологической безопасности в системе биологической и химической безопасности // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2009, том 13, с. 118-121
13. Остроумов С.А., Орлов С.Н., Тодераш И.К., Данилова В.Н., Ермаков В.В., Зубкова Е.И., Камнев А.Н., Колесов Г.М., Котелевцев С.В., Крупина М.В.,Сапожников Д.Ю., Сизов А.Д., Смуров А.В., Соломонова Е.А. Изучение накопления мембраноактивных и генотоксичных металлов в водных беспозвоночных и растениях: перспективы для мониторинга и новых технологий ремедиации // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2008, том 13, с. 129-130.
14. Ворожун И.М., Горшкова О.М., Демина Л.Л., Зубкова Е.И., Камнев А.Н., Клюшников В.Ю., Колесов Г.М., Котелевцев С.В., Крупина М.В., Лазарева Е.В., Нагдалиев Ф.Ф., Остроумов С.А. Использование организмов для целей контроля, охраны и реабилитации (ремедиации) водной среды // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2008, том 13, с. 47-48
15. Ostroumov S.A., Kotelevtsev S.V., Ermakov V.V., Glazer V.M., Gorshkova O.M., Jovanovic L., Kamnev A.N., Kolesov G.M., Lazareva E.V., Matorin D.N., Novikov K.N., McCutcheon S., Panin M.S., Poklonov V.A., Sadchikov A.P., Sheleikovsky V.L., Shestakova T.V., Shpigun O.A., Sizov A.D., Smurov A.V., Soldatov A.A., Solomonova E.A., Toderas I.K., Tropin I.V., Zhbanov A.E., Zoubkov E.I. Studying chemico-biotic interactions in the biosphere: pollutants including membranotropic and genotoxic xenobiotics as well as nanomaterials // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, vol.18, 2013, p. 78-80.
16. Остроумов С.А., Поклонов В.А., Котелевцев С.В., Шестакова Т.В., Демина Л.Л., Шелейковский В.Л. Средоулучшающие фитотехнологии: Micranthemum umbrosum и другие водные макрофиты как фактор снижения содержания в воде тяжелых металлов // Технологии живых систем. 2013. Т. 10. № 1. С. 53-57.
17. Biological Effects of Surfactants. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis (London, New York), 2006, 280 pages.
Also: Ostroumov S.A. Inhibitory analysis of top-down control: new keys to studying eutrophication, algal blooms, and water self-purification. – Hydrobiologia. 2002, vol. 469, p. 117-129; Ostroumov S. A.Basics of the molecular-ecological mechanism of water quality formation and water self-purification. Contemporary Problems of Ecology, 2008, Volume: 1, Issue: 1, Pages: 147-152; DOI: 10.1134/S1995425508010177; Johnson M. E., S. A. Ostroumov, J. F. Tyson and B. Xing. Study of the interactions between Elodea canadensis and CuO nanoparticles // Russian Journal of General Chemistry, 2011.Volume 81, Number 13, 2688-2693, DOI: 10.1134/S107036321113010X;
in preparation: Membranotropic ecotoxicants; toxicology of nanomaterials;
7. Publications of educational materials, improving university education: biological education, environmental education (Учебно-методические публикации, учебные пособия, публикации, рекомендованные в качестве учебных материалов):
Bibliography (selected examples):
Kotelevtzev S.V., Nagdaliev F.F., Sadchikov A.P. Bio-assay and bioindication at ecological analysis of the environment. Publishers: Alteks, Moscow, 2011, 174 p. (in Rus.).
Kotelevtsev S.V., Matorin D.N., Sadchikov A.P. Ecological-Toxicological analysis of plant communities in aquatic ecosystems. Altex Press, Moscow. 2012. 182 p. (in Rus.).
Novikov K.N., S.V. Kotelevtsev, Yu.P.Kozlov. The free-radical processes in biological systems under the influence of environmental factors. - Moscow: Publishing House of People's Friendship University, 2011. - 199 p. ISBN 978-5-209-03659-3. (in Rus.).
Maximov G.V., Orlov S.N. [book] 1994 Transport of calcium ions under axon functioning: mechanisms and regulation. Moscow State Univ. Publ., Moscow, 87 p. (in Rus.).
Остроумов С.А., Котелевцев С.В. О роли и месте концепций экологической безопасности в системе биологической и химической безопасности // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2009, том 13, с. 118-121.
Олескин А.В., Карташева Е.Р., Ботвинко И.В., Остроумов С.А., Лукьянов А.С., Шульга Е.Н. Гуманитарная биология и экология: учебно-методическое пособие для средней общеобразовательной школы, лицеев, колледжей, университетов /под ред. проф. А.В.Олескина. – М.: Издательство Московского университета, 2011. -96 с.: илл. – (МГУ – школе); ISBN 978-5-211-06183-5; Усл.п.л. 6,0; Уч.-изд.л. 4,65. Тираж 500 экз. В книге – глава: С.А.Остроумов. Охрана биоразнообразия и экологическая этика с.60-72. Программа « МГУ-школе».Учебно-методич пособие. Рекомендовано Российским сектором (подкомиссией) Комиссии по Биологическому Образованию (Commission for Biological Education, CBE ) Международного Союза биологических наук (International Union of Biological Sciences ) ЮНЕСКО.
Остроумов С.А., Котелевцев С.В., Козлов Ю.П. Концепция учебного курса по проблемам химического загрязнения среды, экотоксикологии и экологической безопасности // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2010, vol.15, c. 103-106.
Остроумов С.А. Программа курса лекций и семинаров по совершенствованию знаний английского языка для научных целей // Ecological Studies, Hazards, Solutions, 2010, vol. 15, c. 106-108.
«Биологический контроль окружающей среды: биоиндикация и биотестирование» / Ред. О.П. Мелехова, Е.И. Сарапульцева. М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2010, 288 с. ISBN 978-5-7695-7033-9. Усл.печ.л. 18,0. Тир. 1500. 60 90/16. Учебное пособие. 3-е изд. [Совместно: О.П.Мелехова, Е.И. Сарапульцева, Т.И.Евсеева, В.М.Глазер, С.А.Гераськин, Ю.К.Доронин, А.А.Киташова, А.В.Киташов, Ю.П.Козлов, И.А.Кондратьева, Г.В.Коссова, С.В.Котелевцев, Д.Н.Маторин, С.А.Остроумов, С.И.Погосян, А.В.Смуров, Г.Н.Соловых, А.Л.Степанов, Н.А.Тушмалова, Л.В.Цаценко]. Допущено Министерством образования и науки РФ в качестве учебного пособия для студентов высших учебных заведений, обучающихся по направлению подготовки "Биология" и биологическим специальностям.
Гусев М.В., Олескин А.В., Карташева Е.Р., Кировская Т.А., Остроумов С.А., Ботвинко И.В., Лукьянов А.С., Каганова З.В., Юдин Б.Г., Шульга Е.Н., Седов А.Е. Терминологический словарь (тезаурус). Гуманитарная биология. М.: Изд-во МГУ. 2009.- 368 с. ISBN 978-5-211-05360-1. Усл.печ.л. 23,0+вкл. 0,5. Тираж 3000. Среди разделов: Биофилософия, экологическая этика (С.А.О.), охрана биоразнообразия (С.А.О.), биоцентризм, этика экспериментов на животных, генетические технологии, нейрохимия и нормы поведения, биомедицинская этика (чл.-корр. РАН Б.Г. Юдин), биоэстетика, биосемиотика. Библиография, включая сайты Интернета - с.342-363. Резюме на англ.яз. – с.364-366 [ = Gusev M.V., Oleskin A.V., Kartasheva E.R., Kirovskaya T.A., Ostroumov S.A., Botvinko I.V., Lukyanov A.S., Kaganova Z.V., Yudin B.G., Shulga E.N., Sedov A.E. Terminological Dictionary (Thesaurus). Humanities-Oriented Biology [=Terminologicheskij Slovar' (Tezaurus). Gumanitarnaya Biologiya]. Moscow University Press. Moscow. 2009. 368 p. ISBN 978-5-211-05360-1. Bibliography including web-sites - p. 343-363. English summary - p. 364-366.]
MODERN ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ITS MAIN MISTAKE
S.A.Ostroumov
Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
The aim of this short communication is to identify the main mistake of modern aquatic ecotoxicology, the main mistake in modern approach to aquatic pollution.
The modern science of today will become the obsolete science of tomorrow. What the contemporary scientists consider modern concepts will become what the scientists of the future days will consider obsolete, out-of-date, pseudoscientific or antiquated, primitive and nave interpretations of facts. This general truth is applicable to the modern concepts of how to deal with aquatic pollution. The modern concept is focused primarily on trying to find out which concentrations of pollutants are ‘toxic’, and which are not toxic. On the basis of this knowledge, the main effort is to limit the input of pollutants to surface aquatic ecosystems, with the aim to have the concentrations of the pollutants at the levels which are not ‘toxic’. The most convincing criterion of toxicity of the pollutant is death or pathology of organisms. This is the basic concept or paradigm of the modern science. This is the modern and nave interpretation of facts of aquatic ecotoxicology, environmental science and ecology.
What is a more advanced approach? It is formulated and explained in the following publications and online materials.
Not only the input of pollutants is important. Equally important is another factor which is underestimated in modern ecotoxicology. This other – underestimated - factor is the hazard of a decrease in efficiency of the ecological machinery of the aquatic ecosystem, namely the ecological machinery of water self-purification. This decrease can be induced by relatively low - innocent in appearance – concentrations of relatively mild pollutants. This decrease is not associated with mortality or morphological pathology of organisms. That is why these relatively low concentrations, and the relatively mild, almost ‘innocent’ pollutants escape the attention of modern scientists and experts.
Example which illustrates the argument formulated above: relatively low, ‘non-toxic’, and definitely non-lethal concentrations of synthetic surfactants (components of detergents and shampoos) induced a decrease in water-filtration by marine bivalve mollusks [1 ], freshwater bivalve mollusks [ 2 ], crustaceans exemplified by daphnia [ 3 ], and by rotifers [ 4 ].
References.
1. Marine mollusks. Inhibition of Mussel Suspension Feeding by Surfactants of Three >Hydrobiologia (2006); Full text free: http://www.scribd.com/doc/45958156
http://www.scribd.com/doc/59544597
http://www.scribd.com/doc/104742811
2. Freshwater mollusks. See the ref.: Responses of Unio tumidus to Mixed Chemical Preparations and the Hazard of Synecological Summation of Anthropogenic Effects. - Doklady Biological Sciences, 2001, v.380, No.1-6; pp.492-495. DOI: 10.1023/A:1012344026176; Full text free: www.scribd.com/doc/49065621
3. Crustaceans. On studying the hazards of pollution of the biosphere: Effects of sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) on planktonic filter-feeders; in: Doklady Biological Sciences (2009);
DOI 10.1134/S0012496609020136; Full text free: http://www.scribd.com/doc/45914806
4. Rotifers. Effect of a Cationic Amphiphilic Compound on Rotifers. - Doklady Biological Sciences. 2003. Vol. 390. P. 252-255. DOI 10.1023/A:1024417903077; http://www.scribd.com/doc/52634169
Additional discussion and comment see at:
Why it matters. FAQ on innovative publications. Environmental_science. New facts on #environmental_hazards. http://5bio5.blogspot.com/2013/01/why-it-matters-faq-on-innovative.html
Why water_quality goes down rapidly. chemical #pollution #eutrophication #algal_blooms water_safety #sustainability, http://5bio5.blogspot.com/2013/01/why-water-quality-goes-down-so-rapidly.html
Why the current measures against water pollution will fail for sure, if the new discoveries are ignored. http://5bio5.blogspot.com/2012/08/why-current-measures-against-water.html
Explanation of the most important, vital, well-cited publications with key innovations on how to protect water quality and to increase environmental safety of water supply. http://5bio5.blogspot.com/2013/05/explanation-of-most-important-vital.html
**
ENDANGERED WATER QUALITY: NEW HAZARDS. DISCOVERY OF HIDDEN HAZARDS AND PARADOX OF LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF CHEMICALS. New data show: low levels of pollutants in water can be as bad as very hightoxic concentrations. Environmental hazards: small amounts of the aquatic pollutants that were studied do not kill organisms of ecosystems, however, they do not make the ecosystem stronger. They do just the opposite: the low non-lethal concentrations of the chemicals in water bring about very bad effects on functioning (vitality) of the entire ecosystem. Namely, the activity of ecosystem in water self-purification goes down. As a result, water quality goes down dramatically. This was discovered in the series of scientific articles: http://5bio5.blogspot.com/2013/03/endangered-water-quality-new-hazards.html
More info:
31 Top Springer Publications (life science, ecology, environmental science, water science, biology: innovations, new facts, new ideas). Full texts free. Also, indexed: Springer Link, Internet service. Selected: http://5bio5.blogspot.com/2012/11/31-publications-life-science-ecology.html
OBTAINING HYBRID MATERIALS BY SOL GEL METHOD IN THE ORGANIC COMPONENT SiO2 SYSTEM
I.Yordanova
Bulgarian academy of sciences, Institute of Catalysis, Bulgarian Acad. of Sciences, Acad. G. Bonchev St., Block 11,1113 Sofia, Bulgaria,
Key words: hybrid biomaterials, sol- gel,Trichosporoncutaneum
I Introduction
Biomaterials is defined as any substance other than adrug, synthetic or natural fabric of origin, which can be use dat any time, in whole or parts of systems are use das a supplementor replacement tissues, organsand body functions. "Sol-gelmethod of synthesis of inorganic-organic biomaterials is wides pread. The inorganic phase isobtained from metalalkoksi dihydrolysis and condensation reactions in the sol-gel process.These hybrids have interesting properties: molecular homogeneity,transparency and flexibility. Sol-gel process is an interesting method for obtaining inorganic phases in inorganic-organic hybrid materials, as is done in the rooms temperature in liquid solutions. This is an excellent method for obtaining transparent and mechanically stable films is also a convenient method for obtaining porous materials. Such hybrids are promising materials for various applications such as optical components, substitutes for SiO2,media and other biological materials. Biomaterial are typical inorganic- organic hybrid material derived (received) from natural organic polymerisation [1,2]. By sol-gel process are prepared homogeneous inorganic oxide materials with desirable properties-h hardness, transparency, chemical resistance, controlled porosity, thermal stability, etc.. The aim of this study are:
¬ Study for obtaining hybrid inorganic-organic materials by sol-gel method in the system SiO2 –gumarabic and SiO2 - a mixture of gumarabic and starch;
¬Study of structural changes in hybrids when changing the amount and type of organic component;
¬Study for immobilization of microorganisms in the result in ghybrid biomaterials for sorption of heavy metal ions. Immobilization of Trichosporon cutaneum R57 through adhesion on hybrid membranes for adsorption from solutions of ions of heavy metals (copper and cadmium).
II Experimental/methodology
The sol-gel synthesis of hybrid materials is carried out using a magnetic stirrer at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. For prehydrolysis inorganic precursor TEOS using water, alcohol and a small amount of acid that serves as a catalyst for the process. After hydrolysis is added and dissolved in hot water acacia gum, the pH of the system is about 2. To change the pH to 6 using phosphate buffer. The resultings ol was poured into the"plate" and dried at50 C.
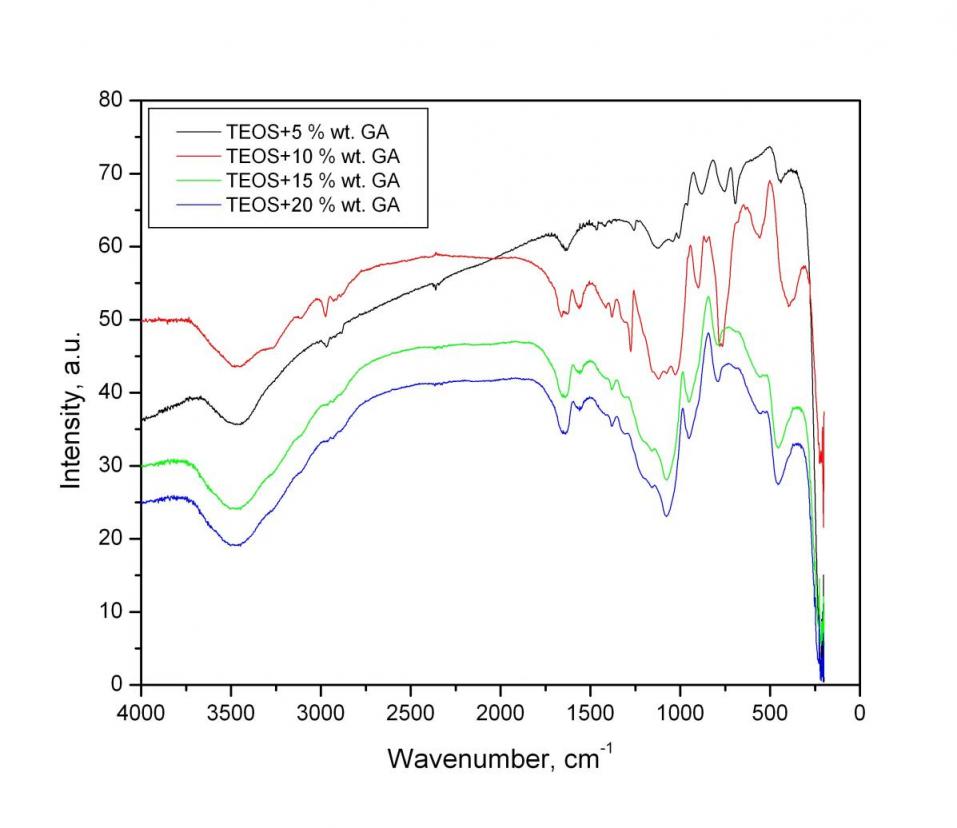
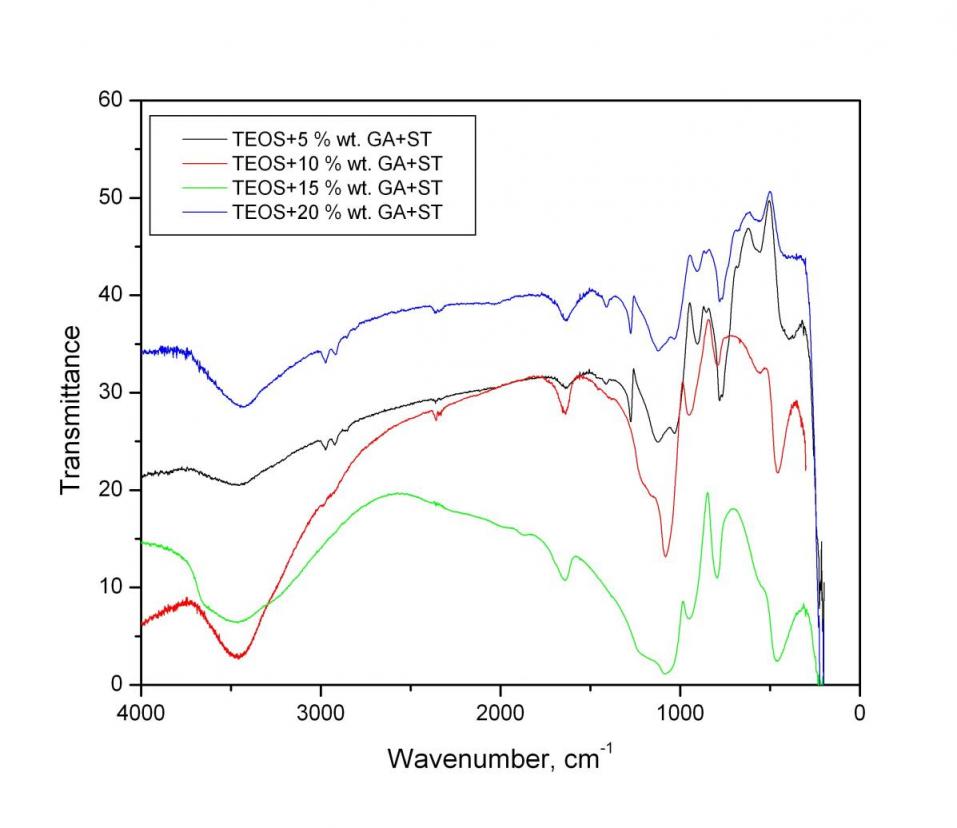
The synthesized samples were characterized by XRD (Bruker D8 Advance, CuK radiation;), FTIR(IR-MATSON 7000 – FTIR Spectrometer;
SEM (JEOL JSM- 5510, JEOL JFC- 1200 fine coater);,AFM(NanoScope Tapping ModeTM)
Trichosporon cutaneum R57 grown in medium with carbon source glucose.
Pre-culture was prepared taking culture agar and inoculated into an Erlenmeyer flask of 500 cm3 of culture medium composed of 90cm3 – environment Andreev and 10 percent glucose – 10 cm3. Add Thiamin - 10mg and biotin- 10l. The strain is cultivated 20 hours. Incubationis carried out on a shaking machine at 220 rpm, 30°C. After the 20th hour, a new Erlenmeyer flask 80 cm3 environment Andreev, 10 cm3 10% glucose, 10 cm3 Pre-culture, thiamine and biotin. In the flask and pre-sterilized hybrid material. 12 hours later added metal cation sat the concentrations: 4 ml of 20m M CdSO4 and 0,25 ml 20 mM CuSO4.5H2O. Using atomic absorption analysis determined the adsorption of metal ions from Trichosporon cutaneum depending on the weather. The change in concentration of the solution is traced in2, 6 and 24 hours.
III Results and discussion
With increasing content of organic component a morphous halo decreases. the registered diffraction maxima is found that there is aflow of processes of structural or dering of hybrid materials
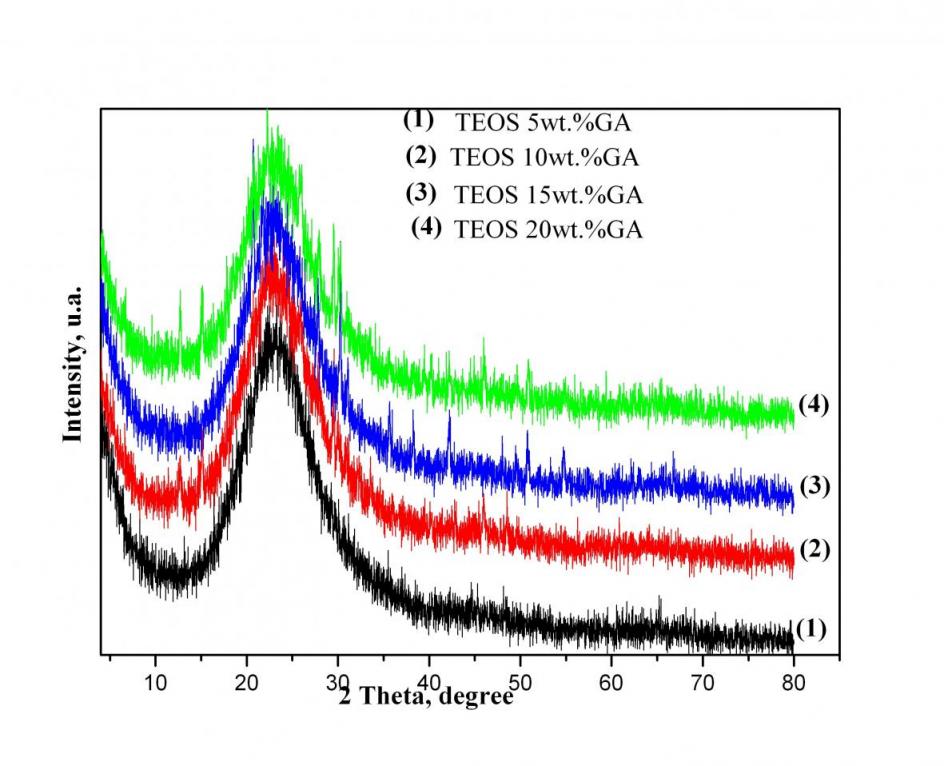
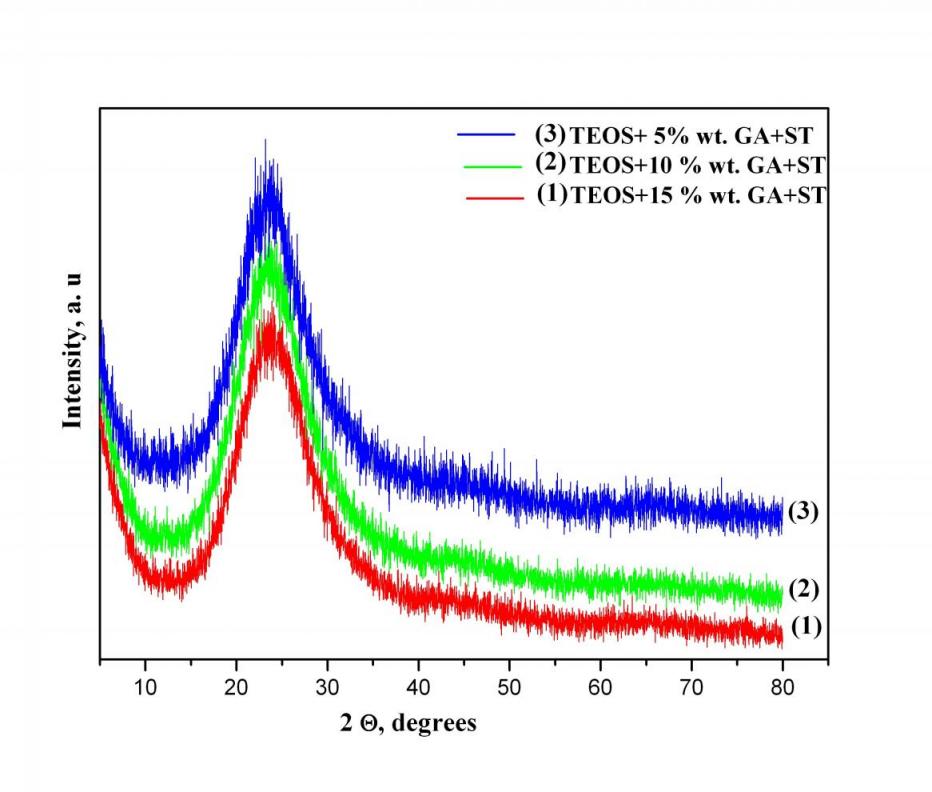
In the spectra of hybrid materials with precursor TEOS observed character is ticbands of SiO2network, some of which overlap with those of gumarabic. The intense peak at 1085 cm – 1 e characteristic of asymmetric fluctuations of Si-O-Si structural network. Siloxane bond (Si-O-Si) is also characterized by band sat 795cm-1 and 460 cm-1. Beach at 960cm-1 and around 560cm-1 are assigned to Si-OH groups with increasing content of gumarabic, decreased gradual ly in intensit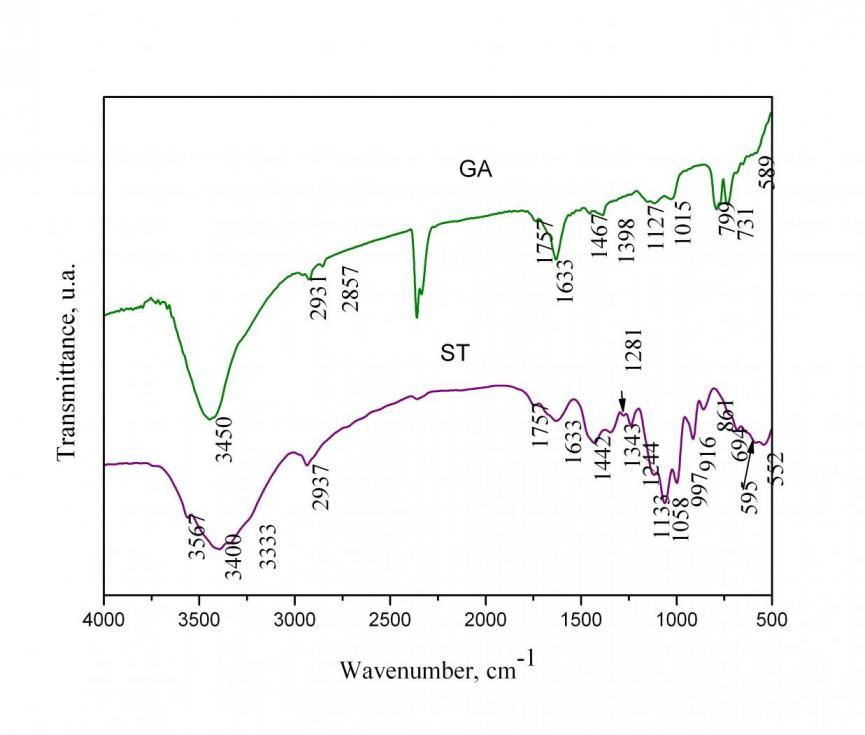
It was found that the samples synthesized with the participation of arabic gum and a mixture of gum arabic and starch with 5 and 10% replacement, the sample surface is smooth and free of microcracks. Increasing the amount of organic compounds leads to the formation of mikroheterogennosti and for samples with 15% gum arabic and starch observed pore size to 3 m, evenly distributed on the surface of the hybrids.
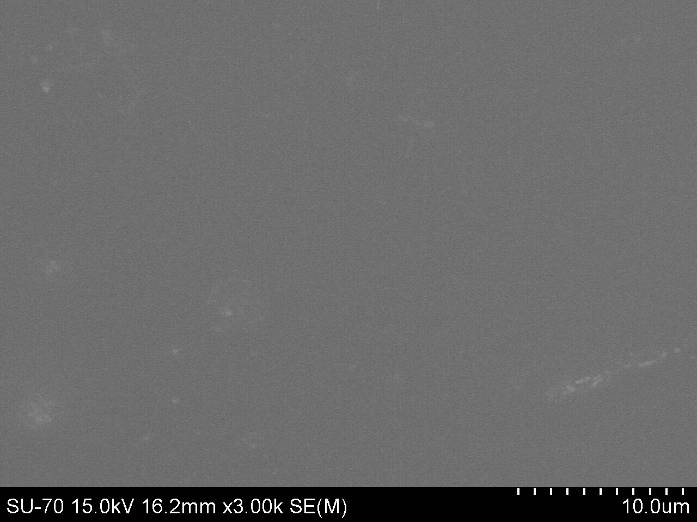
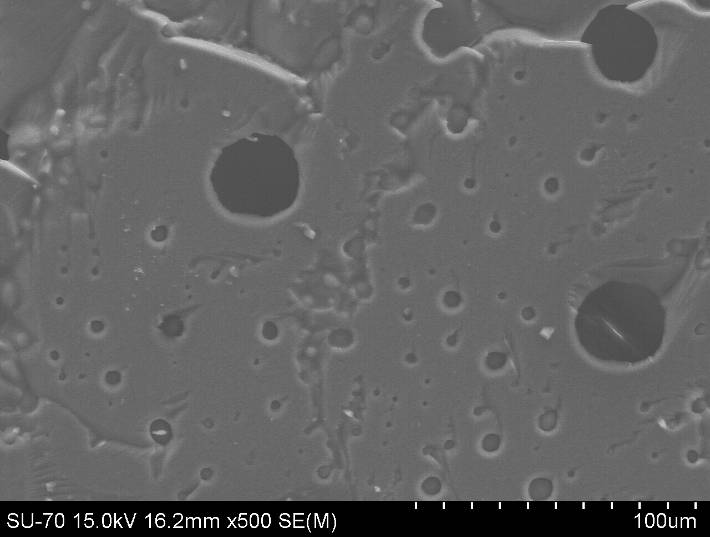
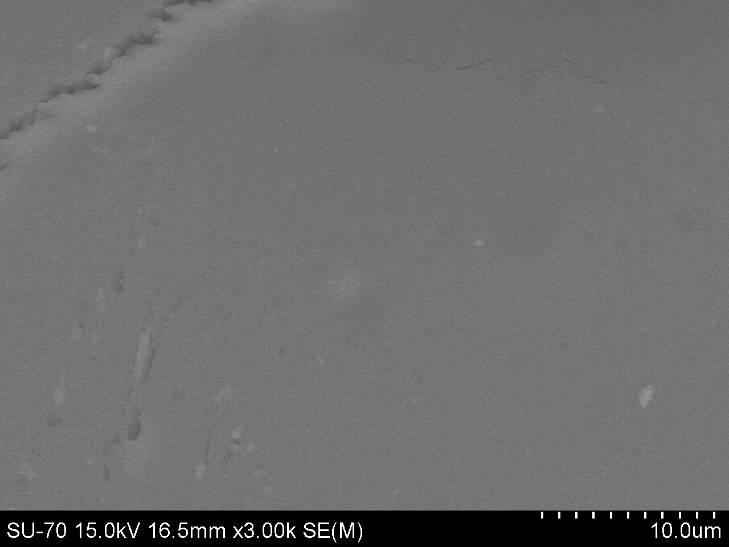
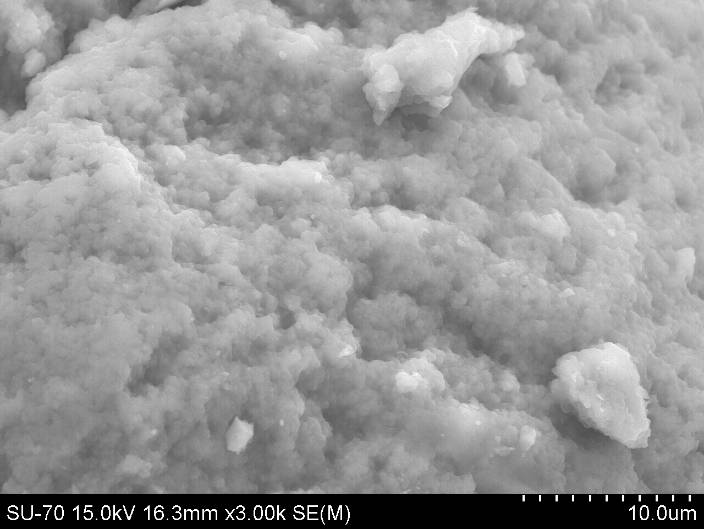




The results show a trend of increasing values of a verageroughness and average height of aggregates and particles synthesized hybrid nanomaterials with increasing amount of organic components.
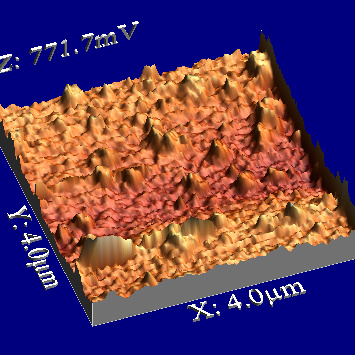
AFM images and analysis of the roughness of the hybrid material containing TEOS and 20wt.% Arabic gum and) 2D; b) 3D; on) 2D analysis of the location of the roughness
IV Conclusions
Series hybrid materials are prepared using by sol gel method. depending on the substances and their concentrations, they can be used for sorption of heavy metal ions and bone implants because they exhibitcy to toxicity.
References
[1] Zh. She, W. Liu, Q. Feng.Mater.Sci.China (2009), 3(3): 241 - 247
[2] G.B.Butler; O’Dristoll, K,F.; Willkes,G. L – Rev. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1994, C34(3), 325 – 373.
УДК 579.26
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ADAPTATIONS ON ACTINOMYCETE FUNCTIONAL ACTIVITY
Zenova G., Kozhevin P., Lubsanova D.
Moscow State University
Temperature is the one of the basic factors influencing on microbe distribution and activity in nature. Understanding of temperature factor effect on living organisms activity has practical meaning, because during this activity microorganisms emit carbon dioxide, one of the greenhouse effect gases responsible for the global warming. So it is important to find out correlation between temperature and functional activity of microorganisms including actinomycetes.
The purpose of our investigation is comparative functional analysis of actinomycetes with different temperature adaptations using multirespirometric testing method (MRT).
Study objects are soil actinomycetes with different temperature adaptations: thermotolerants, mesophiles and psychrotolerants. We used MRT method to register intensivity of consumption of different substrates (mannitol, sucrose, histidine) by these three temperature groups. All data were handled by the methods of multivariate statistics – cluster and discriminant analyses.
Even at a first glimpse we saw the differences in consumption activity between actinomycetes: psyhrotolerants were found to be most active especially the one more psychrophylic in relation to mannitol. Cluster analysis shows that thermotolerants form special cluster apart from mesophiles and psychrotrophs. This is confirmed by the discriminant analysis. Special study of actinomycetes with high temperature adaptations helped to differentiate moderate thermophiles which formed separate cluster from true thermophiles and thermotolerants.
Thus we can suppose that econiches of thermophile, thermotolerant, mesophile and psychrotolerant actinomycetes differ not only by the temperature factor but also by som3999339e other factors reflecting spectra of consumable resources.
НЕКОТОРЫЕ НОВЫЕ ФАКТЫ И КОНЦЕПЦИИ В РАЗВИТИИ
ВОДНОЙ И ОБЩЕЙ ЭКОЛОГИИ
Абакумов В.А., Богатырев Л.Г., Горшкова О.М., Ермаков В.В., Зубкова Е.И., Йованович Л., Котелевцев С.В., Криксунов Е.А., Крупина М.В., Куликов В.Ф., Сизов А.Д., Тодераш И.К., Тропин И.В., Шелейковский В.Л., Шестакова Т.В.
SOME NEW FACTS AND CONCEPTS IN DEVELOPMENT OF AQUATIC AND GENERAL ECOLOGY
Abakumov V.A., Bogatyrev L.G., Gorshkova O.M., Ermakov V.V., Zubkova E.I., ovanovich L., Kotelevtsev S.V., Kriksunov E.A., Krupina M.V., Kulikov V.F., Sizov A.D., Toderash I.K., Tropin I.V., Shelekovski V.L., Shestakova T.V.
Институт глобального климата и экологии Росгидромета и РАН, Москва, РФ
Московский государственный университет им. М.В.Ломоносова, Москва, РФ
Институт геохимии и аналитической химии им. В.И.Вернадского РАН,
Москва, РФ
Институт зоологии АН Молдовы, Кишинев, Moldova
Университет Альфа, Белград, Сербия, Serbia
Институт проблем экологии и эволюции имени А. Н. Северцова РАН, Москва, РФ
Главный ботанический сад РАН, Москва, РФ
Abstract: Review. In this paper, some of achievements and innovations in studies of aquatic ecology and adjacent areas of science are analyzed. The discussion covered selected examples of specific publications on relevant issues of general ecology, ecotoxicology, water quality, limnology, biological oceanography, hydrobiology, biocoenology.
Key words: water quality, aquatic, ecosystems, self-purification, filter-feeders, ecosystem function, bivalves, mollusks, mussels, bioassay, testing, environmental hazards, surfactants, detergents.
В последние годы в работах многих авторов получены существенные факты о структуре и функционировании экосистем, в том числе водных (например, [1-8]), см. таблицу 1.
Среди многих работ в этой области есть серия работ, которую представляется необходимым прокомментировать. Это следующие работы.
В статье [9] впервые сформулирована новая концепция водной экосистемы. Эта концепция выявила аналогию водной экосистемы с таким биореактором, для которого, согласно концепции автора, характерно сочетание нескольких свойств: 1) крупные размеры; 2) диверсификация (в его состав входят многие виды организмов, выполняются одновременно много функций); 3) несет функцию формирования качества воды и самоочищения воды.
Предложена новая концептуализация комплексного контроля численности планктона, новые экспериментальные данные о нарушении контроля при химическом загрязнении [10].
Впервые определен элементный состав пеллет водных моллюсков, сделана количественная оценка их роли в потоках химических элементов через водные экосистемы [11].
Впервые выявлено негативное воздействие синтетического моющего средства на фильтрационную активность пресноводных двустворчатых моллюсков [12].
Впервые сформулированы две новые концепции и предложены новые экологические термины: 1) двухуровневый синергизм; 2) синэкологическое суммирование [13].
Впервые выявлен вклад токсических веществ в явление эвтрофирования пресноводных и морских водных систем [14]. Впервые на этой основе предложено новое решение проблемы эвтрофирования.
В публикации [15] изложены факты, которые выявили новое о ключевой роли сохранения биоразнообразия: в этой работе впервые доказан двусторонний характер причинно-следственных связей между сохранением биоразнообразия водных организмов и качеством воды [15].
Обнаружен новый тип действия химических загрязняющих веществ. Тем самым выявлен новый вид опасности поллютантов водной среды. Этот новый вид экологической опасности при воздействии загрязняющих веществ: опасность нарушения связей между пелагиалью и бенталью в водных экосистемах [16].
Введено новое понятие ‘экологическая ремедиация’ и установлен новый факт: ингибирование процессов экологической ремедиации как результат действия химического загрязняющего вещества [17].
Впервые выявлено и доказано, что катионное поверхностно-активное вещество (КПАВ) обладает негативным действием на мидий: вызывает ингибирование фильтрации воды. Это доказывает, что КПАВ являются опасными загрязнителями воды [18]. В этой работе открыто ингибирующее воздействие ПАВ ТДТМА 0.3 – 5 мг/л на фильтрацию воды мидиями (а именно, в данном случае – гибридными мидиями, получившимися в результате гибридизации Mytilus edulis M. galloprovincialis) из природной популяции в Северной Атлантике.
В ряде статей сделаны некоторые обобщения, которые полезны для изучения и водных, и наземных экосистем. Примеры таких обобщений приведены ниже.
В статье [19] сформулирована новая система критериев для выявления экологической опасности антропогенных воздействий (в том числе химического загрязнения среды) на организмы (на живую природу, на биоту).
Впервые за несколько лет дано современное, логически непротиворечивое, достаточно простое определение термина «экосистема»; впервые после В.Н. Сукачева проведено обновление определения термина «биогеоценоз» [20].
Инновационный анализ выявил новые стороны и положительной, и отрицательной экологической роли химических веществ - их участие в поддержании и нарушении механизма биосферы [21].
Работы серии [9-21] получили положительную оценку специалистов и цитируются в научной литературе [22-33]. В дальнейшем упомянутые работы могут быть использованы как основа для дальнейших исследований в области экологии и гидробиологии, в разработке научных основ сохранения и устойчивого использования экосистем и водных ресурсов, в экологическом образовании.
Таблица 1. Примеры выявления новых фактов о структуре и функционировании экосистем.
Table 1. Discovery of new facts on structure and function of ecosystems